
A Sound Blaster or compatible sound card and speakers recommended.  Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows NT 4.0 system software. Pentium III 1GHz processor-based PC or faster, with a hardware-accelerated video card.
Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP, or Windows NT 4.0 system software. Pentium III 1GHz processor-based PC or faster, with a hardware-accelerated video card. 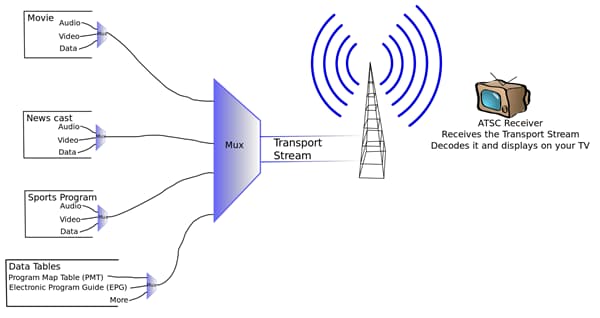 500MHz G4 processor-based computer or faster. QuickTime 6 or later QuickTime 7 or later or QuickTime 6 or 7 Pro. Note that the QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component will not demux audio and video, nor will it enable audio transcoding. By transcoding your MPEG-2 video into other formats, it can be used in new forums, such as on the web, on CD-ROM, or on DV tape. The QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component allows the transcode of MPEG-2 video from both multiplexed and elementary video streams. Transcoding video content: Now your MPEG-2 video content can be imported into QuickTime Pro and exported to other formats such as MPEG-4, the new international standard for Internet media, QuickTime Movie, or DV Stream, to name a few. With QuickTime and the QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component, your clients and reviewers can view your MPEG-2 streams on either a Mac or Windows-based PC, and provide feedback. Professional content production: Throughout the professional content production process, many approvals and progress checks are necessary. The QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component is perfectly suited for professional and semi-professional content creators with projects such as: Note: If you wish to transcode MPEG-2 video content into other formats, QuickTime Pro or an application built upon the QuickTime export architecture is necessary. You need only QuickTime Player and the MPEG-2 Playback Component to view MPEG-2 content. QuickTime Pro is not necessary for playback of MPEG-2 content with the MPEG-2 Playback Component.
500MHz G4 processor-based computer or faster. QuickTime 6 or later QuickTime 7 or later or QuickTime 6 or 7 Pro. Note that the QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component will not demux audio and video, nor will it enable audio transcoding. By transcoding your MPEG-2 video into other formats, it can be used in new forums, such as on the web, on CD-ROM, or on DV tape. The QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component allows the transcode of MPEG-2 video from both multiplexed and elementary video streams. Transcoding video content: Now your MPEG-2 video content can be imported into QuickTime Pro and exported to other formats such as MPEG-4, the new international standard for Internet media, QuickTime Movie, or DV Stream, to name a few. With QuickTime and the QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component, your clients and reviewers can view your MPEG-2 streams on either a Mac or Windows-based PC, and provide feedback. Professional content production: Throughout the professional content production process, many approvals and progress checks are necessary. The QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component is perfectly suited for professional and semi-professional content creators with projects such as: Note: If you wish to transcode MPEG-2 video content into other formats, QuickTime Pro or an application built upon the QuickTime export architecture is necessary. You need only QuickTime Player and the MPEG-2 Playback Component to view MPEG-2 content. QuickTime Pro is not necessary for playback of MPEG-2 content with the MPEG-2 Playback Component. 
Apple’s QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component is compatible with both QuickTime 6 and QuickTime 7. Apple’s QuickTime MPEG-2 Playback Component for Mac OS X, Mac OS 9, and Windows is an add-on to QuickTime or QuickTime Pro provides the ability to import and play back MPEG-2 content, including both multiplexed (also known as muxed, where the audio and video tracks are interleaved together into one track) and non-multiplexed (also known as elementary) streams.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
